This content originally appeared on Telerik Blogs and was authored by Jonathan Gamble
Use Form Actions in Angular with AnalogJS for streamlined form submission, validation and state management.
All the big meta frameworks have Form Actions, and now, so does Angular! Progressive enhancement in Form Actions enables forms to function reliably with basic HTML for all users while adding advanced features like client-side validation and dynamic interactivity for those with modern browsers and JavaScript support.
TL;DR
Form Actions allow you to handle form submissions to the server in a structured way in Angular. Validation and state management are simple, and you only need to add a server file and bind a few events to the client Analog component in Angular. Handling form submission to the server is a breeze.
Single File Component (SFC)
I translated the Analog Form Server Actions example to use the .analog or .ag file extensions. This allows you to create a single file component, similar to Vue or Svelte. It magically compiles to a regular Angular component.
Enable
Make sure the experimental flag is enabled.
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig(({ mode }) => ({
build: {
target: ['es2020'],
},
resolve: {
mainFields: ['module'],
},
plugins: [
analog({
ssr: false,
static: false,
prerender: {
routes: [],
},
// this should be enabled <-----
vite: { experimental: { supportAnalogFormat: true } },
nitro: {
preset: 'vercel-edge'
}
}),
],
}));
Pages Directory
The pages directory functions as the file-based router. It is similar to NextJS’s app directory or SvelteKit’s routes directory.
Create the Server File
In Analog, you need to have your routes in the pages directory. If you want to add a server action, create a file with the same name as .server.ts.
Newsletter
Our newsletter component will be newsletter.server.ts.
import {
type PageServerAction,
redirect,
json,
fail,
} from '@analogjs/router/server/actions';
import { readFormData } from 'h3';
export async function action({ event }: PageServerAction) {
const body = await readFormData(event);
const email = body.get('email');
if (email instanceof File) {
return fail(422, { email: 'Invalid type' });
}
if (!email) {
return fail(422, { email: 'Email is required' });
}
if (email.length < 10) {
return redirect('/');
}
return json({ type: 'success' });
}
New Functions
readFormData– An async function to get the form data from the form action, as typeFormDatafail– Will return an error and call theonError()function on the frontendredirect– Will send a redirect request to the frontendjson– Will return values to the frontend and call theonSuccess()function
This is much simpler than Svelte, which it closely mimics.
Analog SFC Makeup
Analog files can eliminate odd decorators in TypeScript and simplify things.
<script lang="ts">
// the JS code here
</script>
<template>
// the angular template
</template>
<style>
// css if you don't use Tailwind
</style>
Angular has a LOT of boilerplate, and this change makes writing in Angular productive again.
Create the Client Interaction
We must name our client file newsletter.page.ag if we want to use Analog SFC’s with the page router.
<script lang="ts">
import { signal } from '@angular/core';
import { FormAction } from '@analogjs/router';
defineMetadata({
imports: [FormAction]
});
type FormErrors =
| {
email?: string;
}
| undefined;
const signedUp = signal(false);
const errors = signal<FormErrors>(undefined);
function onSuccess() {
signedUp.set(true);
}
function onError(result: FormErrors) {
errors.set(result);
}
</script>
<template>
<section class="flex flex-col gap-5">
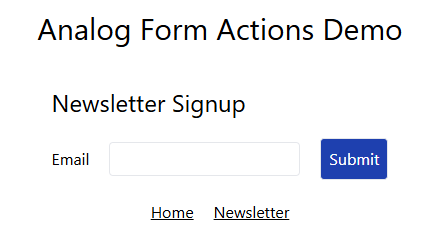
<h3 class="text-2xl">Newsletter Signup</h3>
@if (!signedUp()) {
<form method="post" (onSuccess)="onSuccess()" (onError)="onError($event)" (onStateChange)="errors.set(undefined)">
<div class="flex gap-5 items-center">
<label for="email"> Email </label>
<input class="border p-1 rounded" type="email" name="email" />
<button class="border bg-blue-800 text-white p-2 rounded" type="submit">Submit</button>
</div>
</form>
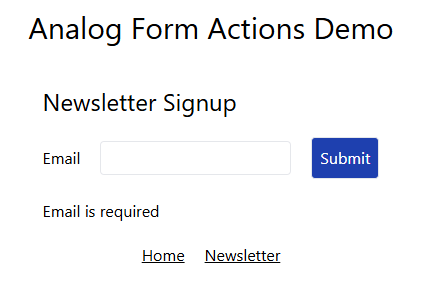
@if( errors()?.email ) {
<p>{{ errors()?.email }}</p>
}
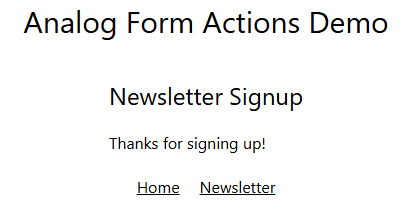
} @else {
<div>Thanks for signing up!</div>
}
</section>
</template>
Import the Form Action
We can use the defineMetadata inside Analog files.
import { FormAction } from '@analogjs/router';
defineMetadata({
imports: [FormAction]
});
Event Bindings
There are three important events to look out for.
(onSuccess)– Gets called when there is no error;json()is used in the form action(onError)– Gets called when there is an error;fail()is called in the form action(onStateChange)– Gets called when the state of the form changes; this is good for resetting the form state
If we pass values from the server, we can use $event to get the event data, aka binding the event.
Signals
We can’t have an Angular app without using signals. We can define our custom FormErrors type and set the errors from the event bindings.
type FormErrors =
| {
email?: string;
}
| undefined;
const signedUp = signal(false);
const errors = signal<FormErrors>(undefined);
Error
The error itself can be handled any way we want.
Success
The success message is generated on the client, but we could also pass a message from the server if necessary.
Verdict?
Analog Form Actions are incredibly easy to use and effective. Building the same app in NextJS or SvelteKit would require much more boilerplate. Thank you, Brandon! Support him if you can.
- Demo: Vercel Edge
- Repo: GitHub
This content originally appeared on Telerik Blogs and was authored by Jonathan Gamble
Jonathan Gamble | Sciencx (2025-04-15T15:09:43+00:00) Angular with AnalogJS Form Actions. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/04/15/angular-with-analogjs-form-actions/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
