This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Ben Mishali
Distributed Architecture Using Node.js
Create highly scalable, fault-tolerant, and flexible applications with distributed architecture using Node.js
Introduction
Distributed architecture refers to the design and implementation of software systems that are composed of multiple interconnected components or nodes, running on different machines or servers, and communicating with each other over a network.
This approach allows for the creation of highly scalable, fault-tolerant, and flexible applications that can handle large volumes of traffic and support a wide range of use cases. Node.js, a popular server-side JavaScript runtime, is a great tool for building distributed architectures, thanks to its asynchronous, event-driven programming model, lightweight and modular architecture, and extensive ecosystem of third-party modules and tools.
Why use distributed architecture with Node.js?
There are many reasons why you might want to use a distributed architecture with Node.js. Some of the main advantages of this approach include:
Scalability
By breaking down your application into smaller, more manageable components that can be distributed across multiple servers, you can easily scale up or down depending on the demands of your users. This means that you can handle increased traffic and load without having to worry about performance issues or downtime.
Fault tolerance
Distributed architectures are designed to be resilient to failures and errors, since components can be replaced or rerouted in case of a problem. This makes your application more reliable and reduces the risk of data loss or system downtime.
Flexibility
With a distributed architecture, you can easily add or remove components as needed, and modify the behavior of your application without having to change the entire system. This makes it easier to adapt to changing requirements or business needs.
Modularity
Node.js is designed to be highly modular, with each module or package providing a specific set of functionalities. This makes it easier to create a distributed architecture where each component performs a specific task or service and can be easily swapped out or upgraded.
Pros and cons
While there are many benefits to using a distributed architecture with Node.js, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.

Here are a few pros and cons to keep in mind:
Pros
- Scalability and fault tolerance
- Flexibility and modularity
- Ability to handle real-time applications and data processing.
- Large ecosystem of third-party modules and tools
Cons
- Complexity and increased development time
- Higher operational costs and infrastructure requirements
- Greater potential for security risks and vulnerabilities
- Requires more advanced knowledge of distributed systems and networking.
💡 But a simplified solution may be offered by tools such as Bit which offers versioning capabilities to track and manage updates. It also comes with a centralized repository for components and documentation, making it easier to understand and manage the state of the system.
Learn more here:
Use Cases
There are many different use cases where a distributed architecture with Node.js can be beneficial. Some common examples include:
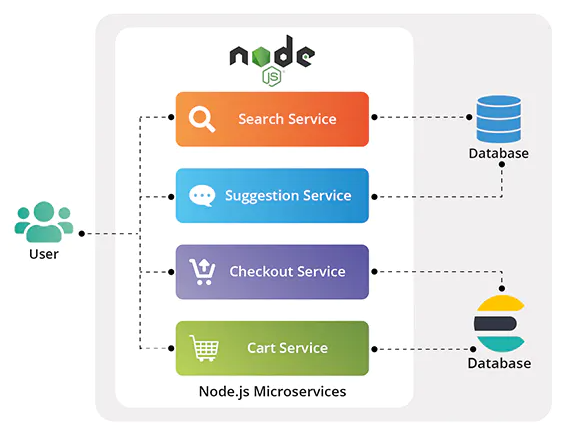
Microservices
In a microservices architecture, different services are broken down into smaller, more manageable components that communicate with each other over a network. Node.js is well-suited for this approach since it provides a lightweight, modular framework that can be easily scaled up or down.
💡 If you’re doing all Node.js-based microservices, a good solution would be using Bit. You can set it up as your main package and dependencies manager and it will abstract you from all the tools on the workflow.
The extra benefit is that you can share internal components (i.e libraries and functions you create for your use case) with other microservices easily. Turning the process of creating and managing common code into a breeze.
Learn more here:
Component-Driven Microservices with NodeJS and Bit
Real-time applications
Node.js is also great for building real-time applications that require instant updates and notifications, such as chat apps, online gaming platforms, or collaborative workspaces.
Data processing
If you need to process large volumes of data in real-time, a distributed architecture with Node.js can help you handle the load and ensure that your application remains responsive.

Third-party modules and tools
There are many third-party modules and tools available for building distributed architectures with Node.js. Here are a few popular options:
Docker
Docker is a containerization platform that allows you to create lightweight, portable containers for your applications. This makes it easy to deploy and manage your application across different servers or environments.

Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that allows you to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of your containers. It provides powerful tools for managing distributed architectures at scale.

RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a message broker that allows you to send and receive messages between different components in your distributed architecture. It provides reliable, asynchronous communication and supports a variety of messaging protocols.

Conclusion
Distributed architecture with Node.js is a powerful approach for building scalable, fault-tolerant, and flexible applications. By breaking down your application into smaller, more manageable components that can be distributed across multiple servers, you can handle increased traffic and load without sacrificing performance or reliability. While there are some potential drawbacks to consider, such as increased complexity and higher operational costs, the benefits of a distributed architecture with Node.js are well worth it for many use cases. With a large ecosystem of third-party modules and tools available, it’s easy to get started building your own distributed architecture with Node.js.
Build Apps with reusable components, just like Lego
Bit’s open-source tool help 250,000+ devs to build apps with components.
Turn any UI, feature, or page into a reusable component — and share it across your applications. It’s easier to collaborate and build faster.
Split apps into components to make app development easier, and enjoy the best experience for the workflows you want:
→ Micro-Frontends
→ Design System
→ Code-Sharing and reuse
→ Monorepo
Learn more:
- Creating a Developer Website with Bit components
- How We Build Micro Frontends
- How we Build a Component Design System
- How to reuse React components across your projects
- 5 Ways to Build a React Monorepo
- How to Create a Composable React App with Bit
- How to Reuse and Share React Components in 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide
Recommendations
- Distributed Systems with Node.js by Thomas Hunter (O’Reilly)
- Design For Scale and High Availability — What Does 100 Million Users On A Google Service Mean? by Shivang
- Monolith to Microservices: Evolutionary Patterns to Transform Your Monolith by Sam Newman

Visit me at ben.dev.io
Distributed Architecture using Node.js was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Ben Mishali
Ben Mishali | Sciencx (2023-04-24T04:21:59+00:00) Distributed Architecture using Node.js. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2023/04/24/distributed-architecture-using-node-js/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
