This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Ibukun OG
In this tutorial, you will create and deploy your own Bitcoin-based token on the Rootstock (RSK) blockchain, using the security and functionality of Bitcoin while using Rootstock's smart contract capabilities.
\ By the end of this guide, you will have a working Bitcoin-based token that is deployed on Rootstock and can be interacted with via a decentralized application (DApp). We’ll cover the following:
\
- Setting up the development environment
- Writing a Bitcoin-based token smart contract using Solidity
- Deploying the smart contract on the Rootstock network
- Interacting with your token through a DApp
Prerequisites
Before we begin:
- Make sure you have Node.js installed.
- Make sure you have NPM (Node Package Manager) installed.
- Hardhat (Ethereum development environment)
- MetaMask (or any web3 wallet)
- A Rootstock (RSK) testnet account
- Basic understanding of Solidity and JavaScript
\ With all of that ready, let’s dive into the setup.
Step 1: Setting Up Your Development Environment
\
\ First, let's create a new project directory for our token and initialize it as a Node.js project.
\
Open your terminal and run the following commands to create a project folder and initialize the project:
\
mkdir bitcoin-token-rsk
cd bitcoin-token-rsk
npm init -y
\
Next, install Hardhat, which we will use to write and deploy the smart contract:
\
npm install --save-dev hardhat
\
Now, initialize Hardhat:
\
npx hardhat
\ Reply to the following Hardhat options when prompted:
\
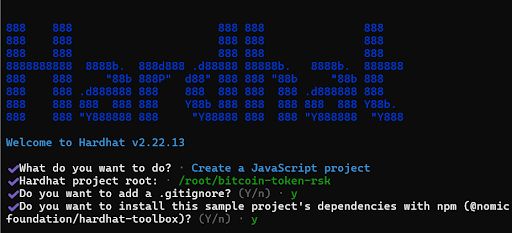
\ \
what do you want to do: SelectCreate a Javascript projectHardhat project root:/root/bitcoin-token-rskDo you want to add a .gitignore?: EnteryInstall Project’s Dependencies with npm: Entery\
Install other necessary dependencies:
\
npm install --save-dev @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox dotenv
\
dotenvwill help us manage environment variables, andhardhat-toolboxcomes with useful plugins for development.\
Create a
.envfile at the root of your project to store your private keys securely:\
PRIVATE_KEY=<your_private_key_here>
\ Now that our environment is set up, we can move on to writing the smart contract.
Step 2: Writing the Bitcoin-based Token Smart Contract
\
\ \ For this token, we'll write a simple ERC-20 contract in Solidity that adheres to the standard of fungible tokens on Ethereum-like networks.
\
In the root directory, create a new folder called
contracts:\
mkdir contracts
\
Inside the
contractsfolder, create a new file calledBitcoinToken.soland add the following contract code:\
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
contract BitcoinToken is ERC20 {
constructor(uint256 initialSupply) ERC20("BitcoinToken", "BTK") {
_mint(msg.sender, initialSupply);
}
}
\ This smart contract uses the ERC-20 standard from OpenZeppelin, which is a well-known and trusted library for Ethereum-based contracts. The contract defines a token named "BitcoinToken" with the symbol "BTK" and mints the initial supply to the deployer's address.
\
Install the OpenZeppelin library:
\
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
\
Step 3: Configuring Hardhat for Rootstock
\
We need to update the hardhat.config.js file to configure the Rootstock network and use our environment variables.
\
Open
hardhat.config.jsand replace its contents with the following code:\
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("dotenv").config();
const { PRIVATE_KEY } = process.env;
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.0",
networks: {
rootstock: {
url: "https://public-node.testnet.rsk.co",
accounts: [PRIVATE_KEY],
chainId: 31,
},
},
};
\ Get the URL from your RootstockRPC Dashboard.
\

\
\
This configuration adds the Rootstock testnet and sets the private key from the .env file.
Step 4: Deploying the Smart Contract on Rootstock
Now that we’ve written the contract, it’s time to deploy it.
\
Inside the root directory, create a new folder called
scripts:\
mkdir scripts
\
Inside the
scriptsfolder, create a file calleddeploy.jswith the following code:\
async function main() { const [deployer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log("Deploying contracts with the account:", deployer.address);
// Use ethers.parseUnits instead of ethers.utils.parseUnits const initialSupply = ethers.parseUnits("1000000", 18); // 1 million tokens
const BitcoinToken = await ethers.getContractFactory("BitcoinToken"); const token = await BitcoinToken.deploy(initialSupply);
await token.waitForDeployment(); // Wait for the deployment to be mined
console.log("BitcoinToken deployed to:", await token.getAddress()); }
main() .then(() => process.exit(0)) .catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exit(1); });
\ This script will deploy the BitcoinToken contract with an initial supply of 1 million tokens, where each token has 18 decimal places.
\
Compile and deploy the contract to Rootstock:
\
npx hardhat compile
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network rootstock
\
Once deployed, the terminal will output the contract address. You can interact with this contract using the deployed address and a web3 wallet like MetaMask.
Step 5: Interacting with the Token
With the contract deployed, we can now interact with it through a DApp. In this section, we will set up a basic frontend to connect to the Rootstock network and interact with the token.
\
Install Next.js and create a new frontend project:
\
npx create-next-app@latest bitcoin-token-dapp
cd bitcoin-token-dapp
\
Install the required web3 libraries:
\
npm install ethers wagmi
\
Inside the
pages/index.jsfile, modify it to add the following code:\
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
export default function Home() {
const [account, setAccount] = useState(null);
const [balance, setBalance] = useState("0");
useEffect(() => {
const loadProvider = async () => {
if (window.ethereum) {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
const accounts = await provider.send("eth_requestAccounts", []);
setAccount(accounts[0]);
const tokenAddress = "<your_token_contract_address>";
const abi = [
"function balanceOf(address) view returns (uint256)",
];
const contract = new ethers.Contract(tokenAddress, abi, provider);
const balance = await contract.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
setBalance(ethers.utils.formatUnits(balance, 18));
}
};
loadProvider();
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h1>BitcoinToken DApp</h1>
<p>Connected account: {account}</p>
<p>Token balance: {balance} BTK</p>
</div>
);
}
This basic DApp connects to MetaMask, retrieves the connected account’s token balance, and displays it.
\
Run the DApp locally:
\
npm run dev
\

\
\
Visit http://localhost:3000 or http://<SERVER-IP>:3000 in your browser, and MetaMask should prompt you to connect your account. After connecting, the DApp will display your Bitcoin-based token balance.
Step 6: Testing and Verifying the Contract
To ensure everything works as expected, we can run some basic tests using Hardhat. Inside the test folder, create a new test file called BitcoinToken.js with the following content:
\
const { expect } = require("chai");
describe("BitcoinToken", function () {
it("should return the correct total supply and balance of deployer", async function () {
const [owner] = await ethers.getSigners();
const BitcoinToken = await ethers.getContractFactory("BitcoinToken");
const token = await BitcoinToken.deploy(ethers.utils.parseUnits("1000000", 18));
expect(await token.totalSupply()).to.equal(ethers.utils.parseUnits("1000000", 18));
expect(await token.balanceOf(owner.address)).to.equal(ethers.utils.parseUnits("1000000", 18));
});
});
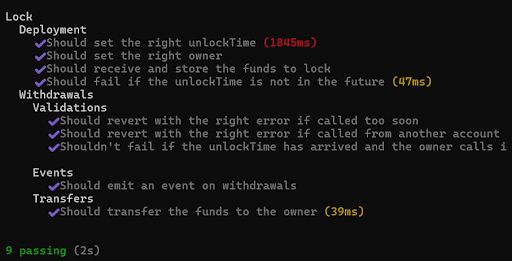
\ To run the tests:
\
npx hardhat test
\
\ \
Troubleshooting
\
If you encounter the following error
\
WARNING: You are currently using Node.js v16.20.2, which is not supported by Hardhat. This can lead to unexpected behavior. See https://hardhat.org/nodejs-versions`
\ Upgrade Node.js: Upgrade your Node.js installation to version 18 or later
\
nvm install 18
nvm use 18
If you encounter the following error
\
Error HH1: You are not inside a Hardhat project.
HardhatError: HH1: You are not inside a Hardhat project.
at main (/root/.npm/_npx/ef9ef3f50c7d7dc1/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/cli/cli.ts:191:13)
at Object.<anonymous> (/root/.npm/_npx/ef9ef3f50c7d7dc1/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/cli/cli.ts:473:1)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1198:14)
at Object.Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1252:10)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1076:32)
at Function.Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:911:12)
at Module.require (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1100:19)
at require (node:internal/modules/cjs/helpers:119:18)
at Object.<anonymous> (/root/.npm/_npx/ef9ef3f50c7d7dc1/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/cli/bootstrap.ts:16:1)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1198:14)
\
Move to the bitcoin-token-rsk directory.
\
cd bitcoin-token-rsk
If you encounter the following error
\
Error HH8: There's one or more errors in your config file:
* Invalid account: #0 for network: rootstock - Expected string, received undefined
To learn more about Hardhat's configuration, please go to https://hardhat.org/config/
HardhatError: HH8: There's one or more errors in your config file:
* Invalid account: #0 for network: rootstock - Expected string, received undefined
To learn more about Hardhat's configuration, please go to https://hardhat.org/config/
at validateConfig (/root/bitcoin-token-rsk/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/core/config/config-validation.ts:374:9)
at loadConfigAndTasks (/root/bitcoin-token-rsk/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/core/config/config-loading.ts:109:3)
at main (/root/bitcoin-token-rsk/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/cli/cli.ts:218:62)
at Object.<anonymous> (/root/bitcoin-token-rsk/node_modules/hardhat/src/internal/cli/cli.ts:473:1)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1364:14)
at Object.Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1422:10)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1203:32)
at Function.Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1019:12)
at Module.require (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1231:19)
at require (node:internal/modules/helpers:177:18)
\ Find the section where you define the "rootstock" network. It should look something like this:
\
module.exports = {
networks: {
rootstock: {
url: "https://public-node.rsk.co",
accounts: ["0x your private key here"] // Replace with your actual private key “process.env.PRIVATE_KEY”
// or use a mnemonic
// accounts: { mnemonic: "your mnemonic phrase here" }
}
},
// ... other configurations
};
\ Install the dotenv package.
\
npm install dotenv
Conclusion
In this guide, you successfully created and deployed a Bitcoin-based token on the Rootstock network.
\ Visit RootStock official documentation for more information.
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Ibukun OG
Ibukun OG | Sciencx (2024-10-25T15:07:35+00:00) Launch a Token on Rootstock: Leverage Bitcoin’s Security with Smart Contracts. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2024/10/25/launch-a-token-on-rootstock-leverage-bitcoins-security-with-smart-contracts/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
