This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Mike Chen
How to fully automate synchronising Bit component updates across multiple Git repositories

Automation is no longer a luxury in modern software development — it’s the backbone of efficient workflows. As teams transition to composable architectures with Bit components, breaking codebases from monorepos into a flexible multi-repo structure becomes possible.
For instance, an organization can maintain a single design system Git repository with reusable components also exported into Bit platform and use these components in different applications having their own Git repositories.
This approach offers unparalleled flexibility but introduces a significant challenge: keeping shared components up-to-date across all dependent projects.
Without proper synchronization, even minor updates can cascade into costly issues. Ripple CI’s webhook feature provides a powerful solution, seamlessly bridging the gap between Bit components and Git-based CI/CD pipelines. It enables teams to automate updates, ensuring consistency and eliminating the need for manual intervention.
Design System and Applications
Let's look into a practical example of separating the design system repository from the application code.
- Design System Repository: The design team maintains a centralized repository for UI components like buttons, modals, and typography, all exported as Bit components. These components are also published into the bit platform for cross-project sharing.
- Application Repositories: Multiple applications consume these components, each maintained in its own repository. These applications rely on the design system components to ensure visual and functional consistency.
Unlike importing an entire design system package, Bit platform provides the flexibility to pick and choose the components you need for the application.
Suppose the design system team fixes a critical bug in a key component, such as a button. Every application must pull the latest version to get the issue fixed. Without automation, teams face two major challenges:
- Manual Effort: Developers in each application repo must manually fetch the updated components from the Bit platform and commit them back to their repository.
- Version Drift: Some applications may delay updates, leading to mismatched versions of components and inconsistent user experiences, especially in microfrontend teams.
Now imagine Ripple CI in action. With its webhook feature, every update to the design system automatically triggers a CI/CD pipeline in each application repository, syncing the latest component versions. This ensures all applications use the most up-to-date components, maintaining consistency across the board.
Manual Synchronization
Without automation, teams like the one above face:
- Lost Time: Developers waste hours manually importing updated components and resolving conflicts.
- Inconsistencies: Applications using outdated components suffer from mismatched visuals or broken functionality.
- Missed Updates: Teams may forget to pull updates entirely, creating technical debt over time.
Suppose the application teams feel they need more control over the component updates. In that case, they can still create a job (e.g. In GitLab, we can create a pipeline job without executing it) whenever an external component gets updated so that the team can decide whether to run when they are ready.
Automating Synchronization: A Step-by-Step Guide
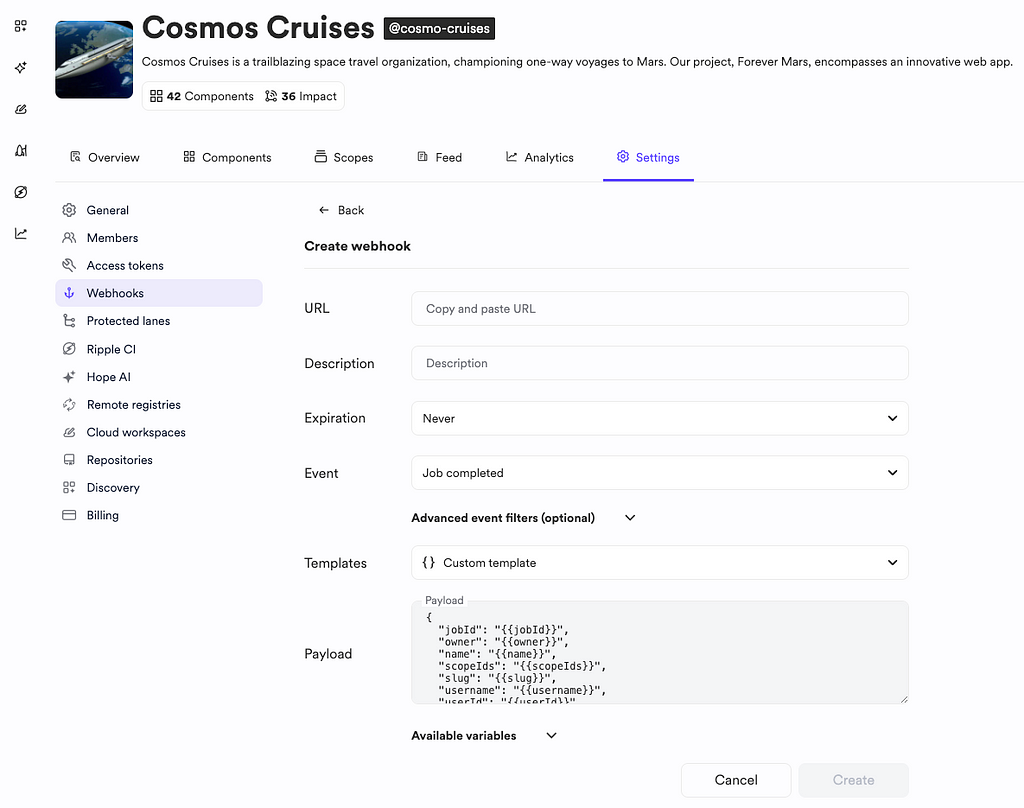
1. Configuring the Design System Repository
The design system repository is the central source of truth for UI components. These components are also exported into a scope in the Bit platform, as in this example.
The team uses Ripple CI to manage updates and releases. To enable synchronization:
- Set up a webhook in Ripple CI triggered by the Released components event.
- Point the webhook to the GitLab pipeline trigger URL for dependent applications:
https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/<project-id>/trigger/pipeline?token=<token>&ref=main
- The default payload template includes critical information about the updated component:
{
"componentName": "{{name}}",
"releaseVersion": "{{version}}",
"scope": "{{scope}}",
"triggeredBy": "{{username}}",
"releaseTime": "{{finishedAt}}"
}- For GitLab, clear the object by removing all the attributes and replacing them with an empty object{} since the Gitlab pipeline we use is not processing these parameters.
2. Setting Up Application Repositories
Each application repository contains a GitLab CI/CD pipeline designed to handle updates from the design system. Here’s an example .gitlab-ci.yml configuration:
image: bitsrc/stable:latest
variables:
GIT_USER_NAME: "<name>"
GIT_USER_EMAIL: "<email>"
dependency-update-job:
stage: build
script:
- |
cd test-ws
gitlab.bit.init
gitlab.bit.dependency-update
github.bit.commit-bitmap
rules:
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"'
- when: manual # Allows manual trigger
This pipeline automatically:
- Imports the updated Bit components and updates their dependencies.
- Commits the changes to the Git repository.
3. Testing the Workflow
Here’s how to test the complete workflow in practice:
- The design team releases a new button component in the design system using bit tag -m "updating button" && bit export .

- After the component build is complete, Ripple CI triggers the webhook to execute the pipeline in GitLab.
- The GitLab pipeline configured in the application repository executes the component update script, ensuring the latest components are integrated.
- The commit-bitmap The script finally commits the component updates to the git repository.
Best Practices when using Webhooks
- Secure Webhooks: Use authentication tokens and HTTPS to protect webhook endpoints from unauthorized access.
- Optimize Payloads: Include only essential data to reduce processing time and avoid unnecessary complexity.
- Error Handling: Monitor webhook activity and set up retry mechanisms for failed requests.
- Thorough Testing: Validate the end-to-end process in a staging environment before deploying to production.
The Ripple Effect: Benefits of Automation
1. Time Savings
Manual syncing is time-consuming and error-prone. Developers have to watch for dependent component updates and be alerted. Ripple CI webhooks eliminate this burden, allowing teams to focus on building features.
2. Consistency Across Applications
Every project receives updates simultaneously, ensuring consistent user experiences.
3. Scalable Workflows
As new applications are added, the same webhook-driven process applies, requiring no additional configuration.
Conclusion: Building a Unified Ecosystem
Ripple CI webhooks revolutionize how teams manage component-driven development. Automating the synchronization of the latest changes to Bit components helps keep its dependents aware of the changes and stay up-to-date.
With Ripple CI, your design system and applications can operate in perfect harmony, freeing your team to focus on what they do best: building exceptional software.
Ready to transform your workflow? Start using Ripple CI webhooks today and experience the power of seamless synchronization!
Learn More
- Git + Bit: Code Meets Components
- Integrating Bit with Gihub Actions, Azure DevOps, Github CI, Jenkins, and more
- The Evolution of Source Control: Svn, Git and Bit
Synchronising Components Updates Between Bit and Git: Using Webhooks was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Mike Chen
Mike Chen | Sciencx (2025-01-23T07:31:15+00:00) Synchronising Components Updates Between Bit and Git: Using Webhooks. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/01/23/synchronising-components-updates-between-bit-and-git-using-webhooks/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
