This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Saleemuddin Khan
🏹 Null Safety in Kotlin
Dodging the Null Pointer Exception, the Kotlin way🤓🤓
➤ Concept of Strict Null Safety in Kotlin
• Safe Call Operator ( ?. ) in Kotlin
• Elvis Operator ( ?: ) in Kotlin
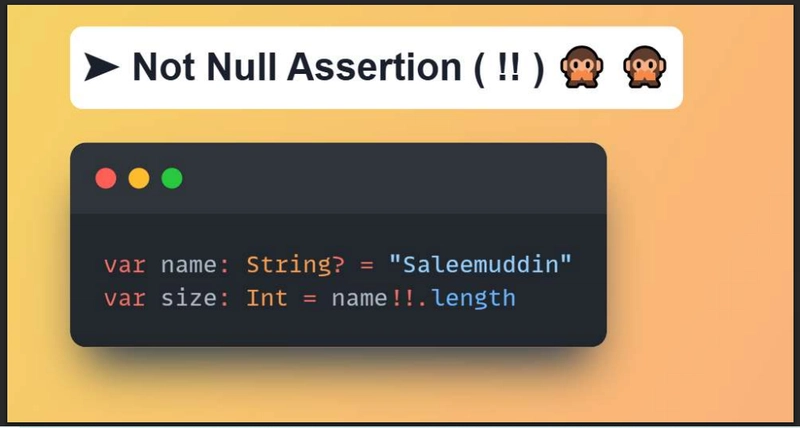
• Not Null Assertion ( !! ) in Kotlin.
- Kotlin allows to store “Null” values in a variable.
- In Kotlin, the variables can be made of Null types by just adding a “?” symbol to the right side of the data type.
- A nullable type variable means it can also hold “Null” as a value in it.
- A non-nullable type variable means that it can not hold “Null” as a value in it.
- The safe call operator is simply a question mark followed by a dot ( ?. )
- The safe call operator in Kotlin, is one of the methods to impose “Null Safety Checks” on the nullable variables.
- If the left-hand side of the operator is null, then it will return null value.
- If the left-hand side of the operator is not null, then it will return the result of the right-hand side expression.
- The elvis operator is represented by a question mark followed by a colon ( ?: )
- The elvis operator in Kotlin, is one of the methods to impose “Null Safety Checks” on the nullable variables.
- If the first operand is not null, then this operand will be returned by the elvis operator.
- If the first operand is null, then second operand will be returned by the elvis operator.
- The Not Null Assertion is represented by a double exclamation mark (!!)
- The Not Null Assertion in Kotlin, is another tool to deal with nullity.
- This operator explicitly casts nullable variables to non-nullable variables.
This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Saleemuddin Khan
Saleemuddin Khan | Sciencx (2025-05-18T13:58:14+00:00) 🚀 Kotlin’s Key Features #1. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/05/18/%f0%9f%9a%80-kotlins-key-features-1/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.