This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Instancing
Table of Links
Method
Experiments
Performance Analysis
Supplementary Material
- Details of KITTI360Pose Dataset
- More Experiments on the Instance Query Extractor
- Text-Cell Embedding Space Analysis
- More Visualization Results
- Point Cloud Robustness Analysis
Anonymous Authors
- Details of KITTI360Pose Dataset
- More Experiments on the Instance Query Extractor
- Text-Cell Embedding Space Analysis
- More Visualization Results
- Point Cloud Robustness Analysis
5 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
5.1 Ablation Study
The following ablation studies evaluate the effectiveness of the relative position-aware components in the two stages.
\ RowColRPA. To evaluate the effectiveness of RowColRPA in the coarse stage, we compare it with different variants, as shown in
\
\ Table 4. The result reveals that incorporating a relative position attribute into the value component yields a modest enhancement of 15%/10%/8% at the top-1/3/5 recall metrics, respectively, when compared to the conventional self-attention mechanism. Incorporating the pooled relative position feature into the query results in nearly the same level of improvement, with a marginally higher increase observed at the top-5 recall rate. In contrast, the novel strategy of integrating a row-wise pooled relative position feature with the query, and introducing a column-wise pooled relative position feature to the key, results in a significant performance boost of 26%/21%/18% against the standard self-attention at the top-1/3/5 recall benchmarks on the validation dataset. This demonstrates the pronounced superiority and efficiency of the proposed RowColRPA in capturing spatial relationships and enhancing retrieval performance.
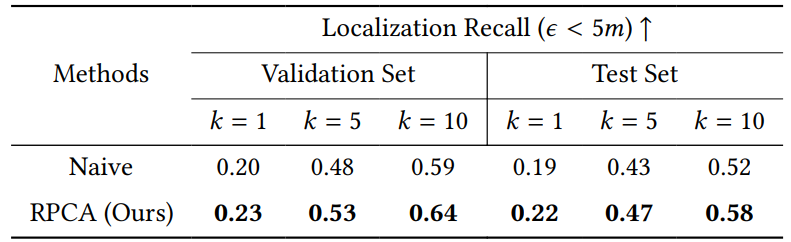
\ RPCA. To analyse the effectiveness of RPCA in the fine stage, we compare it with the variant using standard cross-attention, as shown in Table 5. The result shows that our RPCA leads to 15%/10%/8% improvement comparing to the standard self-attention at top-1/5/10 localization recall rates, respectively. It demonstrates the capability of RPCA to effectively integrate relative position information during the multi-modal fusion process, thereby enhancing localization accuracy.
5.2 Qualitative Analysis
In addition to the quantitative metrics, we also offer a qualitative analysis comparing the top-1/2/3 retrieved cells by Text2Loc [42] and IFRP-T2P, as depicted in Fig. 6. In the first column, the result indicates that both models can retrieve cells with the described instances. However, there are notable differences in their accuracy with respect to the spatial relation descriptions provided. Specifically, for the “beige parking” instance, which is described as being located to the west of the cell, the retrieval result of Text2Loc inaccurately places it to the e ast of the cell centers. Conversely, IFRP-T2P correctly locates this instance to the east of the center, aligning with the given description. In the second column, the text hints describe that the pose is on-top of a “dark-green vegetation” and is north of a “dark-green parking”. For Text2Loc, the parking is found to the north of the cell center in the top-1/2 retrieved cells, and the vegetation is located at the margin area of the top-1/2/3 retrieved cells, discrepant from the text description. For IFRP-T2P, however, the parking appears on the south of the cell center in the top-1/2 retrieved cells, and the vegetation appears on the center of the top-1/2/3 retrieved cells, which matches with the text
\
\
![Figure 6: Comparison of the top-3 retrieved cells between Text2Loc [42] and IFRP-T2P. The numbers within the top-3 retrieval submaps denote the center distances between the retrieved submaps and the ground-truth, with “n/a” indicating distances exceeding 1000 meters. Green boxes highlight the positive submaps, which contain the target location, whereas red boxes delineate the negative submaps that do not contain the target.](https://cdn.hackernoon.com/images/fWZa4tUiBGemnqQfBGgCPf9594N2-ya033mv.png)
\ \ description. Notably, in both cases, only the third retrieved cell by IFRP-T2P exceeds the error threshold. This evidence solidifies the superior capacity of IFRP-T2P to interpret and utilize relative position information in comparison to Text2Loc. More case studies of our IFRP-T2P are provided in the supplement material.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Lichao Wang, FNii, CUHKSZ (wanglichao1999@outlook.com);
(2) Zhihao Yuan, FNii and SSE, CUHKSZ (zhihaoyuan@link.cuhk.edu.cn);
(3) Jinke Ren, FNii and SSE, CUHKSZ (jinkeren@cuhk.edu.cn);
(4) Shuguang Cui, SSE and FNii, CUHKSZ (shuguangcui@cuhk.edu.cn);
(5) Zhen Li, a Corresponding Author from SSE and FNii, CUHKSZ (lizhen@cuhk.edu.cn).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Instancing
Instancing | Sciencx (2025-07-16T11:00:08+00:00) Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Relative Position-Enhanced Transformers. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/07/16/qualitative-and-quantitative-analysis-of-relative-position-enhanced-transformers/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
