This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars
Table of Links
Background
Data
Empirical Results
C. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Gas Fee
D. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Blob Gas Priority Fee
E. Rollup Transaction Dynamics
4.3 Rollup transactions
Understanding user interactions within the blockchain ecosystem is crucial, especially in response to changes introduced by EIP-4844. This section examines the impact of the upgrade on the number of rollup transactions that are posted on Ethereum, which reflects the level of rollup activity. Additionally, we consider user delay— the time it takes for transactions to be securely settled in Ethereum— as a crucial aspect of rollup security.
\ We analyzed six major rollups, comprising three optimistic rollups (Arbitrum One, Optimism, Base) and three ZK rollups (Starknet, zkSync Era, Linea), with a focus on transaction volume and user delays. Our principal observations are:
\ (1) All six rollups showed a marked increase in transaction volume, with Base experiencing a particularly significant rise, more than tripling its previous count.
\ (2) User delay, the time lag between the creation of rollup blocks and their posting on Ethereum, increased notably in four rollups. Conversely, Arbitrum and zkSync Era achieved significant improvements, witnessing reductions in their delay times.
\ (3) The variability in user delay times also saw a notable increase, except in Arbitrum, where it remained more stable.
\ 4.3.1 Number of rollup transactions. To retrieve the number of transactions posted on Ethereum, we decoded the batch transactions on Ethereum sent by rollups. Table 13 indicates a substantial increase across six rollups. Notably, Base experienced a significant rise of 224%, while Arbitrum, Optimism, and Starknet each saw increases exceeding 70%. This overall uptick suggests that the reduced fees resulting from EIP-4844 may have incentivized a greater volume of transactions on rollups.
\ However, attributing this increase solely to EIP-4844 would be premature without considering pre-existing growth trends. Rollups were already experiencing rapid expansion prior to the protocol’s
\
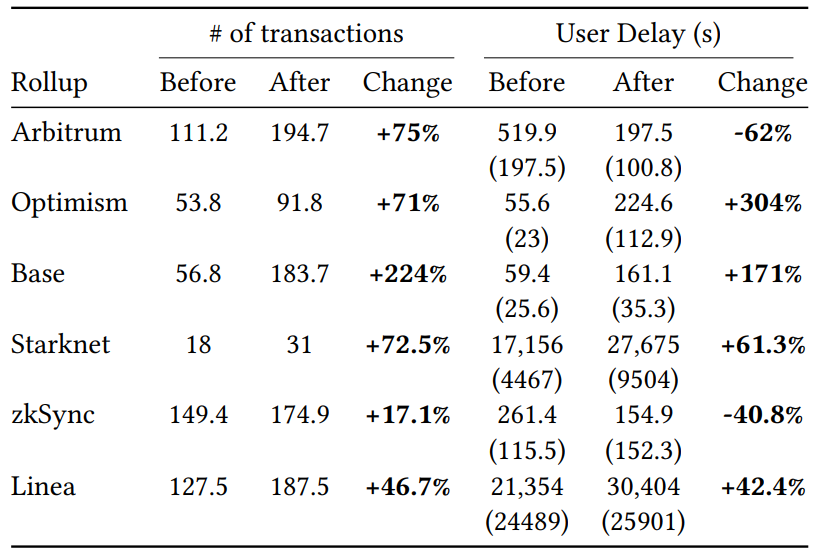
\ implementation, and the observed increases might partly reflect the ongoing market growth rather than the effects of EIP-4844 alone.
\ To rigorously assess the specific impact of EIP-4844, we employed a Regression Discontinuity Design (RDD) for each rollup.
\
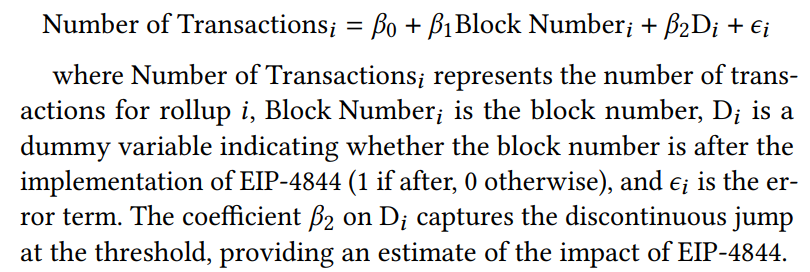
\ The results, presented in Table 3, show statistically significant increases in transaction volumes for most rollups, affirming the effect of EIP-4844. However, Linea exhibited a negative coefficient for ‘D’, suggesting that increases in Linea’s transaction volumes may not be directly attributable to the effects of EIP-4844.
\
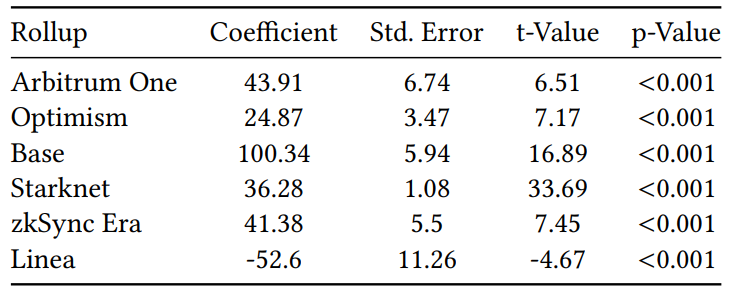
\ 4.3.2 Delay of L2 transactions. To comprehensively assess the delays experienced by users of rollup transactions, we define the user delay metric as follows. This metric calculates the average timing difference between when rollup transactions are created and when they are committed on Ethereum.
\
\
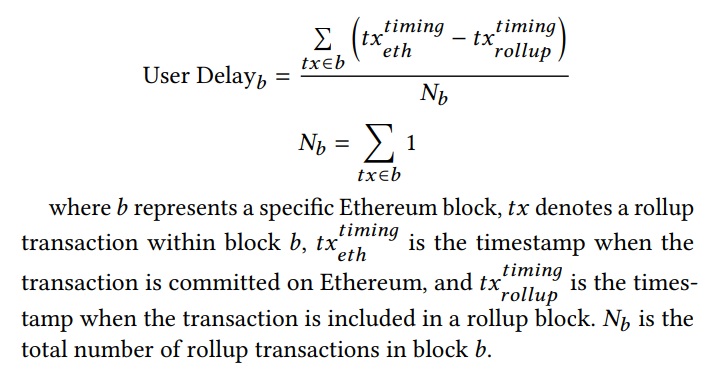
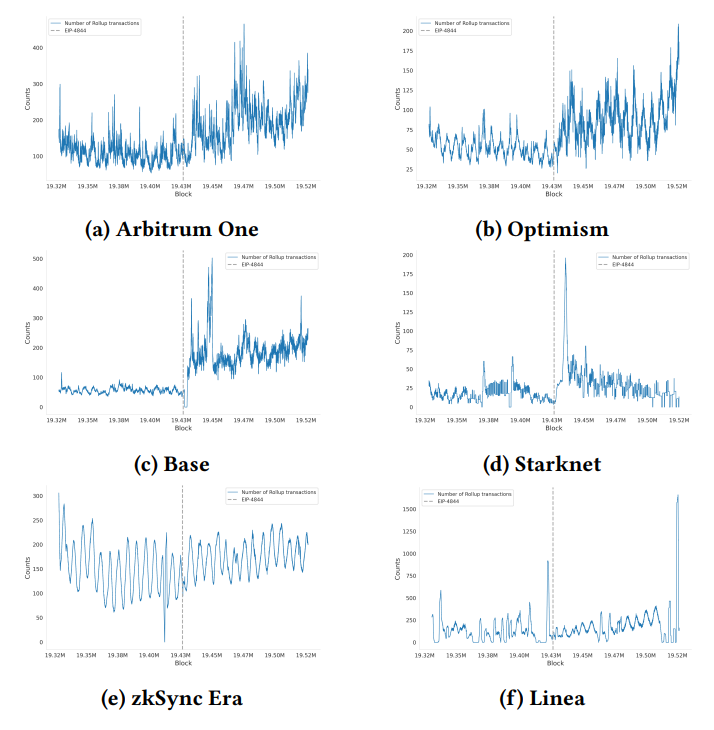
\ Figure 14 illustrates the distribution of user delays for each rollup before and after the implementation of EIP-4844. Despite an increase in the number of rollup transactions, four out of six rollups showed an increase in user delay. Notably, Arbitrum One saw a significant decrease in user delay by 62%, and zkSync by 40%, indicating faster transaction settlement times. Conversely, other rollups exhibited notable increases in delay.
\ Increased user delays indicate that users often experience longer wait times before their transactions are settled on Ethereum, requiring them to maintain trust in the rollup operators until their transactions are committed. A potential cause for increased delay could be rollups waiting to fill blobs to their capacity of 128KiB before committing them.
\ The standard deviation of user delay is also a crucial indicator of predictability in waiting time, essential for user assurance regarding transaction security. Table 2 indicates that the standard deviation of user delays increased in all rollups except Arbitrum, suggesting that
\
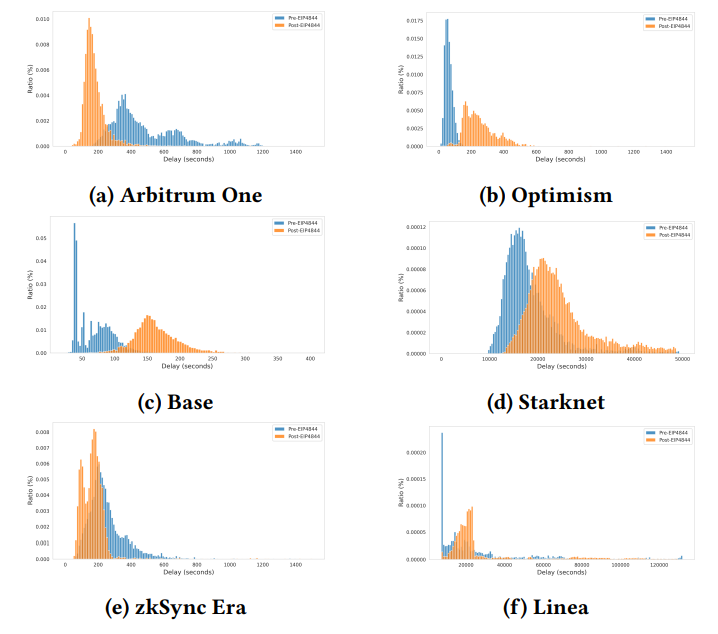
\ users frequently face longer waiting times for their transactions to be settled on Ethereum.
\ While increasing transaction volumes that rapidly fill the 128KiB capacity may help reduce these delays, rollups with smaller or infrequent transactions might still face extended waiting times. This issue highlights the need for blob sharing protocols among different rollups to hasten transaction commit times and enhance user experiences by shortening wait periods.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Seongwan Park, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea (sucre87@snu.ac.kr);
(2) Bosul Mun, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea (bsbs8645@snu.ac.kr);
(3) Seungyun Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(4) Woojin Jeong, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(5) Jaewook Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(6) Hyeonsang Eom, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(7) Huisu Jang (Corresponding author), Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under ATTRIBUTION-NONCOMMERCIAL-NODERIVS 4.0 INTERNATIONAL license.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars
EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars | Sciencx (2025-08-13T15:00:07+00:00) Rollup Transactions Exploded After EIP-4844 — But There’s a Catch. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/08/13/rollup-transactions-exploded-after-eip-4844-but-theres-a-catch/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
