This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars
Table of Links
2 Model and Warmup
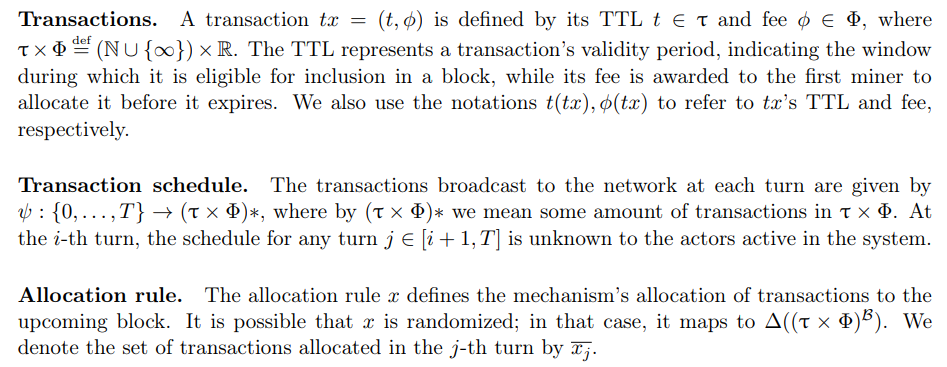
Our game proceeds in T ∈ N turns. At each one, a set of new transactions is broadcast to the network by users, and a miner is chosen to create the upcoming block. The miner, assumed to be profit-maximizing, has the sole authority to decide which transactions to allocate to its block, among the set of valid transactions which were not allocated beforehand.
\ We proceed to formally define the model. A summary of all notations appears in Appendix C.
2.1 Blockchain Model
Blocks. Blocks have a predefined maximal capacity of B ∈ N∪ {∞} identically-sized transactions. We focus on the case where B = 1
\
2.2 The Miner
We examine a far-sighted miner who plans the allocation of transactions to the next T blocks.
\ Allocation strategy. The miner’s allocation strategy is given by its allocation function x.
\ Discount factor. Miners may prefer to receive revenue earlier rather than later, as dependent on the economy’s interest rate. For example, this could be due to the profit which a miner participating in a PoS mechanism can obtain by staking funds, or a Proof-of-Work (PoW) miner can make by using its funds to purchase additional mining equipment. This is captured by the miner’s discount factor, denoted by λ ≤ 1.
\
\

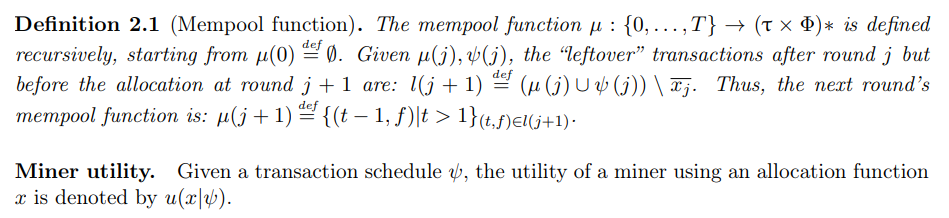
\ \ Mempool. The miner stores valid transactions that were not yet allocated to a block or expired in a data structure called the memory pool (mempool). Transactions which are not allocated to the upcoming block have to wait at least one more block until being mined, but some may become ineligible for inclusion as dependent on their TTL, which decreases by 1 with each passing turn. We define a mempool function that outputs the set of transactions viable for inclusion in each block.
\
\
\
\
\

\
\
\

\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Yotam Gafni, Weizmann Institute (yotam.gafni@gmail.com);
(2) Aviv Yaish, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem (aviv.yaish@mail.huji.ac.il).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars
EScholar: Electronic Academic Papers for Scholars | Sciencx (2025-10-13T19:54:06+00:00) How Auction Theory Shapes Smarter Blockchain Transaction Fee Models. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/10/13/how-auction-theory-shapes-smarter-blockchain-transaction-fee-models-2/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
